Quickstart
What is Azure Virtual Network?
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) provides the means for Azure cloud resources such as virtual machines to securely communicate with each other as well as the rest of the internet and on-premises resources. Using VNet to create a private network gives you control over network filtering, routing, and other key pieces of the network infrastructure. Given an Azure virtual network, you can do things like assign a public IP, assign a load balancer, and handle outbound connections. VNets are ideal for developers deploying on Azure resources who want fine-grained control over network management.
New Relic Azure Vnet integration
New Relic's integration for Azure Virtual Network reports metric data about your virtual networks (VNets), like packets dropped per second or bytes forwarded per second. It also collects data about the status and configuration of your account. The selection of dashboards include:
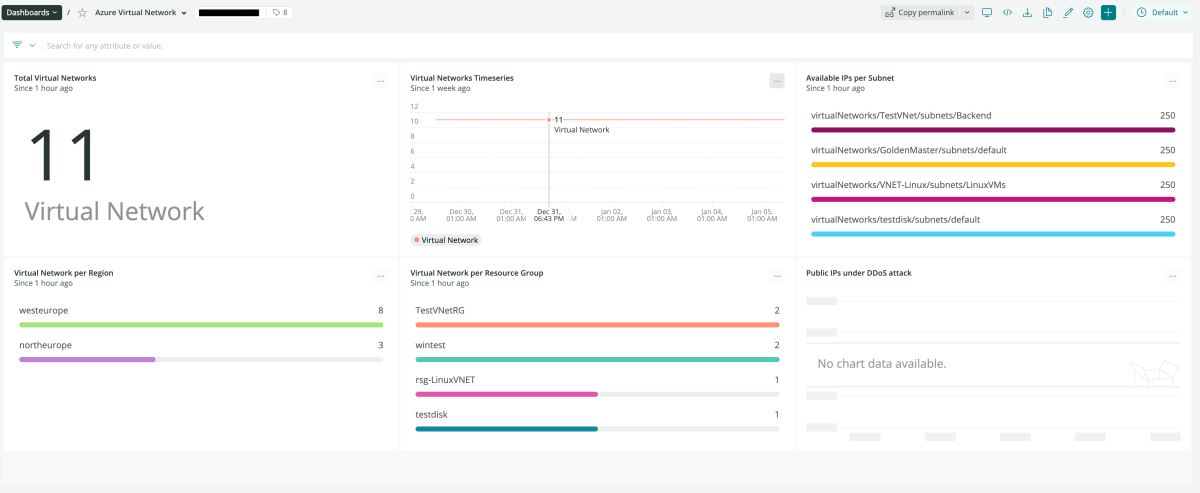
- Total virtual networks: The total number of virtual networks currently live
- Virtual networks time series: Displays the fluctuation of the total number of virtual networks over a series of timepoints
- Virtual network per region: Displays the virtual networks within a specific geographic region
- Public IPs under DDoS attack: Quickly identify which IPs on the network may be experiencing a DDOS attack
- Virtual network per resource group: Shows the number of virtual networks deployed within each resource group
Why monitor Azure Virtual Network with New Relic?
Having insight into Azure virtual network performance is key to keeping network systems healthy and reliable. Virtual networks are often vulnerable to attack, so continuous monitoring of IP requests and understanding which IPs may be experiencing a distributed denial of service (DDOS) attack can be critical for initiating a proactive response. The virtual network time series display can give insight into fluctuations in network health and uptime within a specified interval and can be useful for drilling down into any deviations from the norm. Finally, being able to understand how virtual networks are distributed across geographic regions can help you pinpoint when a particular region is being underserved and deploy network resources accordingly.
Need help? Visit our Support Center or check out our community forum, the Explorers Hub.